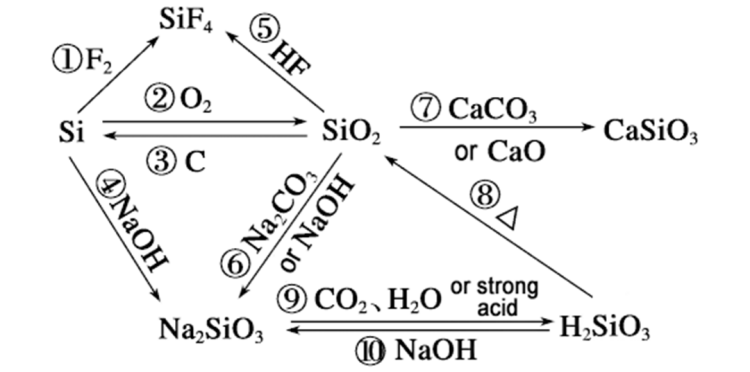
Why the reaction rate of silicon and sodium hydroxide can surpass that of silicon dioxide can be analyzed from the following aspects:
Difference in chemical bond energy
▪ Reaction of silicon and sodium hydroxide: When silicon reacts with sodium hydroxide, the Si-Si bond energy between silicon atoms is only 176kJ/mol. The Si-Si bond breaks during the reaction, which is relatively easier to break. From a kinetic point of view, the reaction is easier to proceed.
▪ Reaction of silicon dioxide and sodium hydroxide: The Si-O bond energy between silicon atoms and oxygen atoms in silicon dioxide is 460kJ/mol, which is relatively high. It takes higher energy to break the Si-O bond during the reaction, so the reaction is relatively difficult to occur and the reaction rate is slow.
Different reaction mechanisms
▪ Silicon reacts with sodium hydroxide: Silicon reacts with sodium hydroxide first by reacting with water to generate hydrogen and silicic acid, then silicic acid reacts with sodium hydroxide to generate sodium silicate and water. During this reaction, the reaction between silicon and water releases heat, which can promote molecular motion, thereby creating a better kinetic environment for the reaction and accelerating the reaction rate.
▪ Silicon dioxide reacts with sodium hydroxide: Silicon dioxide reacts with sodium hydroxide first by reacting with water to generate silicic acid, then silicic acid reacts with sodium hydroxide to generate sodium silicate. The reaction between silicon dioxide and water is extremely slow, and the reaction process basically does not release heat. From a kinetic point of view, it is not conducive to a rapid reaction.
Different material structures
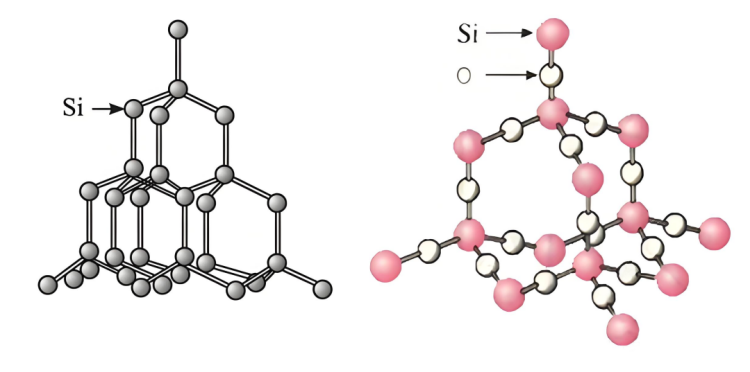
▪ Silicon structure: Silicon has a certain crystal structure, and there are certain gaps and relatively weak interactions between atoms, making it easier for sodium hydroxide solution to contact and react with silicon atoms.
▪ Structure of silicon dioxide: silicon dioxide has a stable spatial network structure. Silicon atoms and oxygen atoms are tightly bound by covalent bonds to form a hard and stable crystal structure. It is difficult for sodium hydroxide solution to penetrate into its interior and fully contact silicon atoms, resulting in difficulty in rapid reaction. Only silicon atoms on the surface of silicon dioxide particles can react with sodium hydroxide, limiting the reaction rate.
Effect of conditions
▪ Reaction of silicon with sodium hydroxide: Under heating conditions, the reaction rate of silicon with sodium hydroxide solution will be significantly accelerated, and the reaction can generally proceed smoothly at high temperatures.
▪ Reaction of silicon dioxide with sodium hydroxide: The reaction of silicon dioxide with sodium hydroxide solution is very slow at room temperature. Usually, the reaction rate will be improved under harsh conditions such as high temperature and concentrated sodium hydroxide solution.
Post time: Dec-10-2024