Nuclear hydrogen production is widely considered the preferred method for large-scale hydrogen production, but it seems to be progressing slowly. So, what is nuclear hydrogen production?
Nuclear hydrogen production, that is, nuclear reactor coupled with advanced hydrogen production process, for mass production of hydrogen. Hydrogen production from nuclear energy has the advantages of no greenhouse gases, water as raw material, high efficiency and large scale, so it is an important solution for large-scale hydrogen supply in the future. According to IAEA estimates, a small 250MW reactor can produce 50 tons of hydrogen per day using high temperature nuclear reactions.
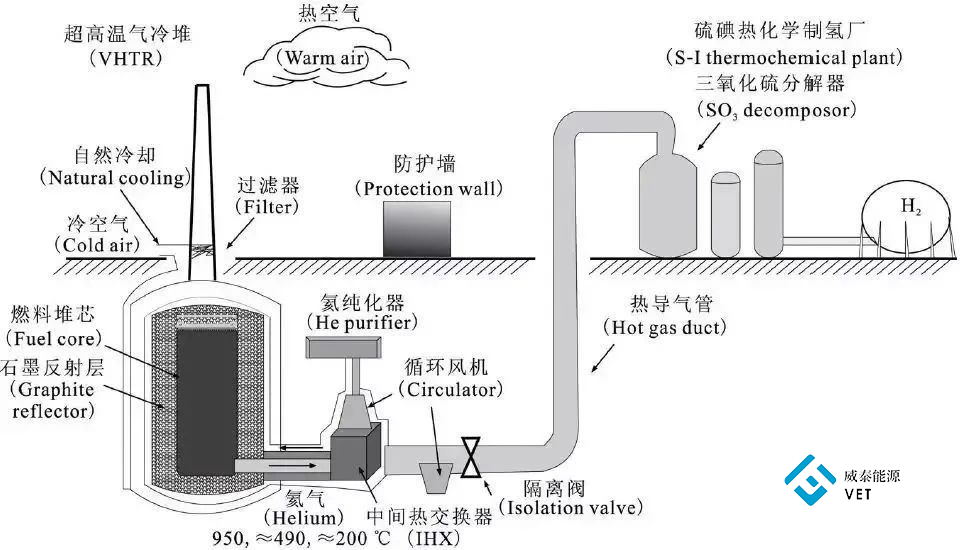
The principle of hydrogen production in nuclear energy is to use the heat generated by nuclear reactor as the energy source for hydrogen production, and to realize efficient and large-scale hydrogen production by selecting appropriate technology. And reduce or even eliminate greenhouse gas emissions. The schematic diagram of hydrogen production from nuclear energy is shown in the figure.
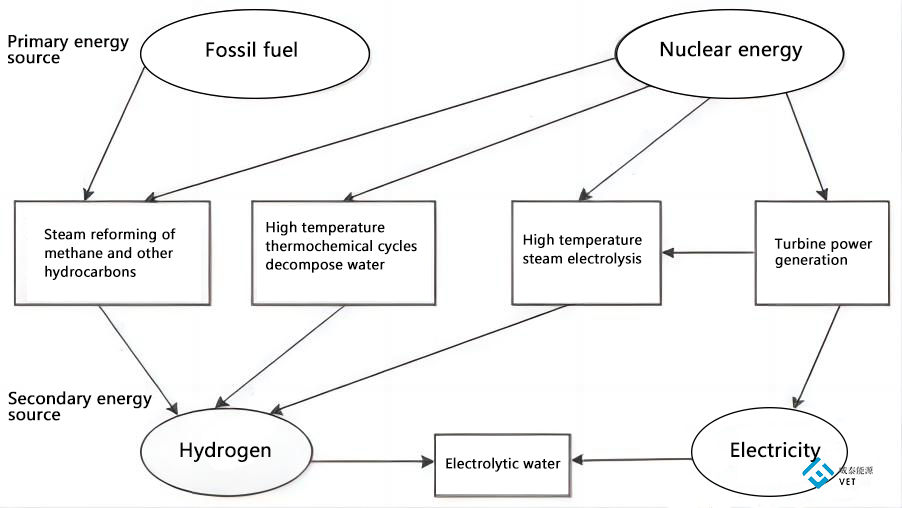
There are many ways to convert nuclear energy to hydrogen energy, including water as raw material through electrolysis, thermochemical cycle, high temperature steam electrolysis hydrogen production, hydrogen sulfide as raw material cracking hydrogen production, natural gas, coal, biomass as raw materials pyrolysis hydrogen production, etc. When using water as raw material, the entire hydrogen production process does not produce CO₂, which can basically eliminate greenhouse gas emissions; Producing hydrogen from other sources only reduces carbon emissions. In addition, the use of nuclear electrolysis water is just a simple combination of nuclear power generation and traditional electrolysis, which still belongs to the field of nuclear power generation and is generally not regarded as a true nuclear hydrogen production technology. Therefore, the thermochemical cycle with water as raw material, full or partial use of nuclear heat and high temperature steam electrolysis are considered to represent the future direction of nuclear hydrogen production technology.
At present, there are two main ways of hydrogen production in nuclear energy: electrolytic water hydrogen production and thermochemical hydrogen production. Nuclear reactors provide electric energy and heat energy respectively for the above two ways of hydrogen production.
Electrolysis of water to produce hydrogen is to use nuclear energy to generate electricity, and then through the water electrolytic device to decompose water into hydrogen. Hydrogen production by electrolytic water is a relatively direct hydrogen production method, but the hydrogen production efficiency of this method (55% ~ 60%) is low, even if the most advanced SPE water electrolysis technology is adopted in the United States, the electrolytic efficiency is increased to 90%. But since most nuclear power plants currently only convert heat to electricity at around 35% efficiency, the final total efficiency of hydrogen production from water electrolysis in nuclear energy is only 30%.
Thermal-chemical hydrogen production is based on thermal-chemical cycle, coupling a nuclear reactor with a thermal-chemical cycle hydrogen production device, using the high temperature provided by the nuclear reactor as a heat source, so that water catalyzes thermal decomposition at 800℃ to 1000℃, so as to produce hydrogen and oxygen. Compared with electrolytic water hydrogen production, thermo chemical hydrogen production efficiency is higher, the total efficiency is expected to reach more than 50%, the cost is lower.
Post time: Feb-28-2023