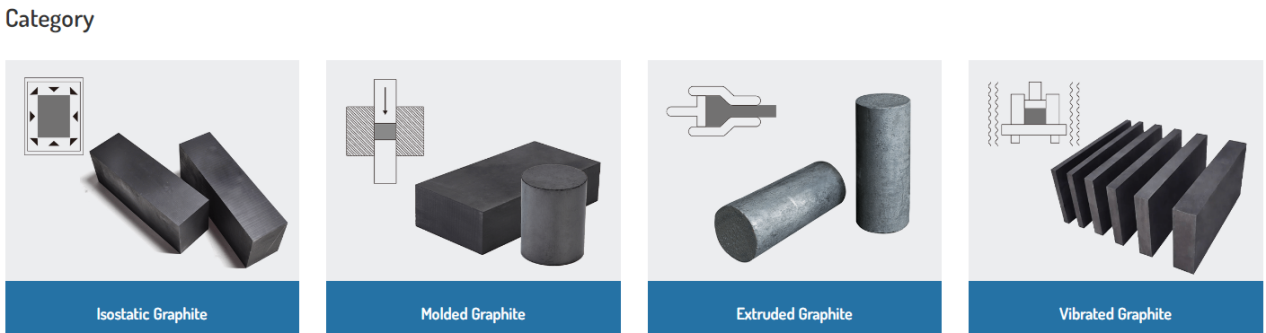
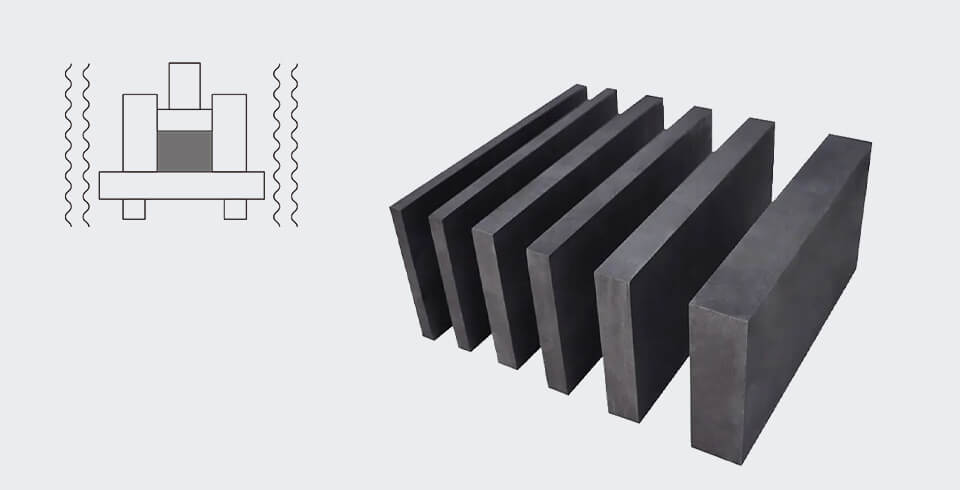
Special graphite is a high purity, high density and high strength graphite material and has excellent corrosion resistance, high temperature stability and great electrical conductivity. It is made of natural or artificial graphite after high temperature heat treatment and high pressure processing and is commonly used in industrial applications in high temperature, high pressure and corrosive environments.
It can be divided into various types including isostatic graphite blocks, extruded graphite blocks, molded graphite blocks and vibrated graphite blocks.
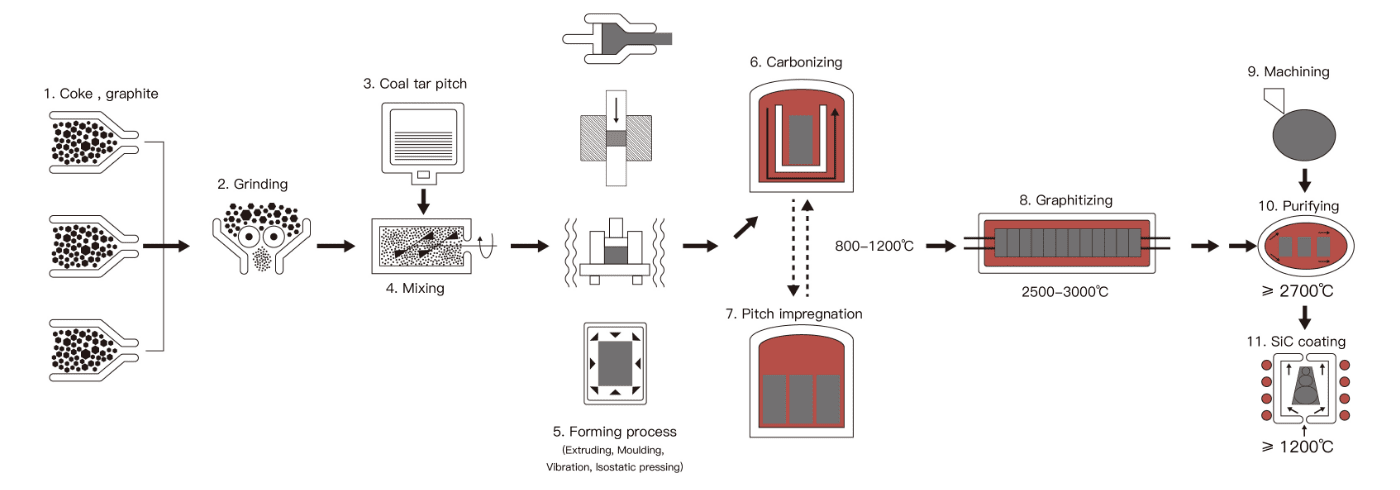
Manufacturing Technologies:
Graphite is a unique non-metallic element composed of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice structure. It is a soft and brittle material that is commonly used in various industrial applications due to its unique properties. Graphite can maintain its strength and stability even at temperatures exceeding 3600 °C. Now let me introduce the production process of special graphite.
Isostatic graphite, made of high purity graphite by pressing, is an irreplaceable material used in the manufacturing of single crystal furnaces, metal continuous casting graphite crystallizers, and graphite electrodes for electrical spark discharge machining. In addition to these main applications, it is widely used in the fields of hard alloys (vacuum furnace heaters, sintering plates, etc.), mining (manufacturing of drill bit molds), chemical industry (heat exchangers, corrosion-resistant parts), metallurgy (crucibles), and machinery (mechanical seals).
Molding Technology
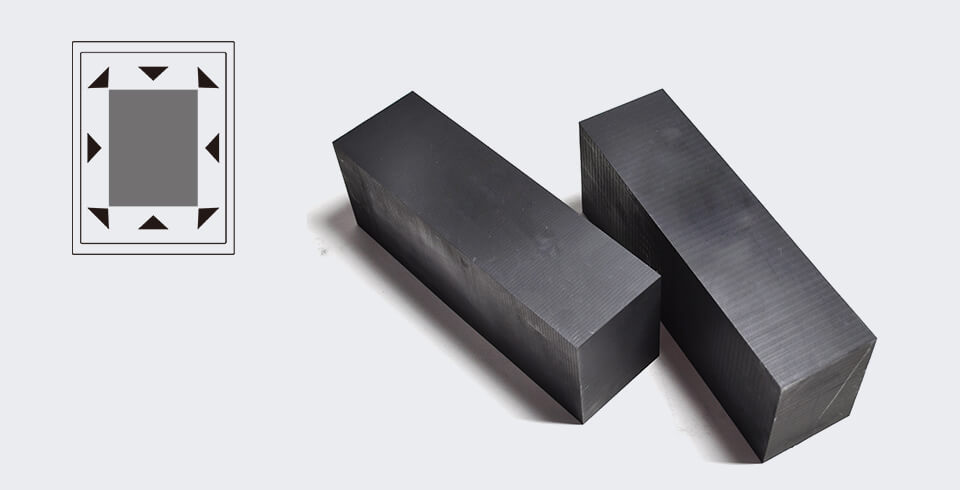
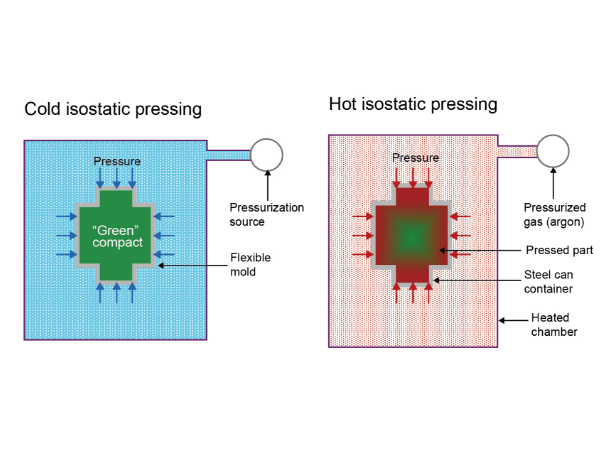
The principle of isostatic pressing technology is based on Pascal’s law. It changes the unidirectional (or bidirectional) compression of the material into multi-directional (omnidirectional) compression. During the process, the carbon particles are always in a disordered state, and the volume density is relatively uniform with isotropic properties. Besides, it is not subject to the height of the product, thus making the isostatic graphite have no or little performance differences.
According to the temperature at which the forming and solidification take place, isostatic pressing technology can be divided into cold isostatic pressing, warm isostatic pressing, and hot isostatic pressing. Isostatic pressing products have a high density, typically 5% to 15% higher than those of unidirectional or bidirectional mold pressing products. The relative density of isostatic pressing products can reach 99.8% to 99.09%.
Molded graphite has outstanding performances in mechanical strength, abrasion resistance, density, hardness and electrical conductivity and these performances can be further improved by impregnating resin or metal.
Molded graphite features good electrical conductivity, high temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, high purity, self-lubrication, thermal shock resistance and easy precision machining, and is widely used in the fields of continuous casting, hard alloy and electronic die sintering, electric spark, mechanical seal, etc.
Molding Technology
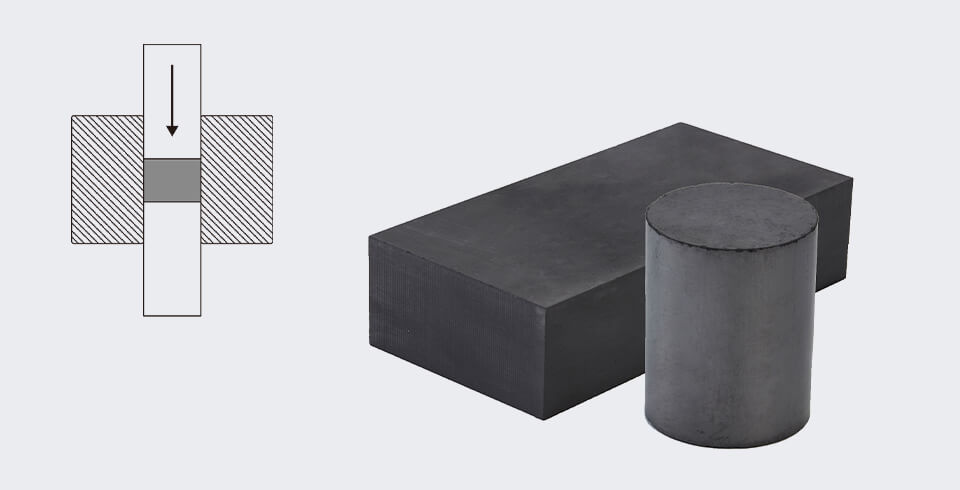
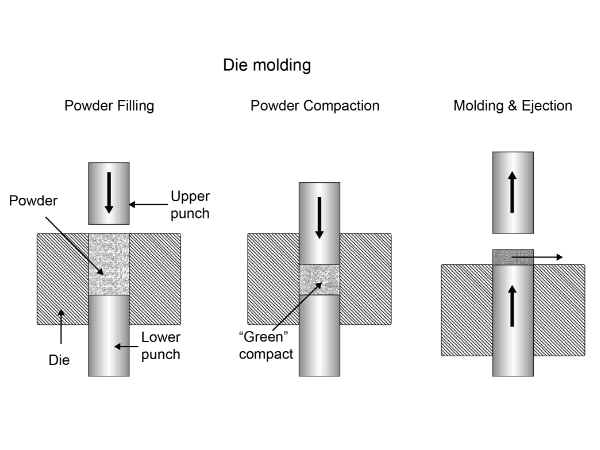
The molding method is generally used to produce small-sized cold-pressed graphite or finely structured products. The principle is to fill a certain amount of paste into a mold of the required shape and size, and then apply pressure from the top or bottom. Sometimes, apply pressure from both directions to compress the paste into shape in the mold. The pressed semi-finished product is then demolded, cooled, inspected, and stacked.
There are both vertical and horizontal molding machines. Molding method generally can only press one product at a time, so it has a relatively low production efficiency. However, it can produce high-precision products that cannot be made by other technologies. Moreover, the production efficiency can be improved through simultaneous pressing of multiple molds and automated production lines.
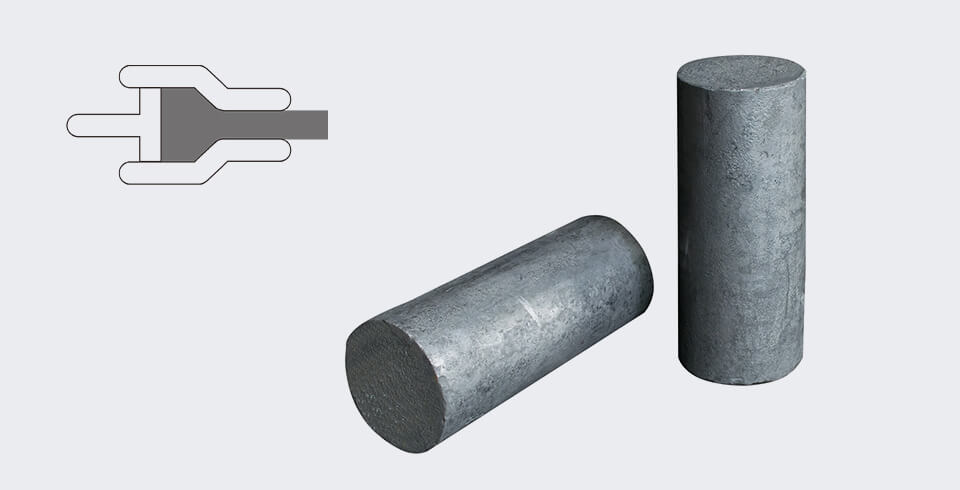
Extruded graphite is formed by mixing high purity graphite particles with a binder and then extruding them in an extruder. Compared with isostatic graphite, the extruded graphite has a coarser grain size and a lower strength, but it has a higher thermal and electrical conductivity.
Currently, most carbon and graphite products are produced by extrusion method. They are mainly used as heating elements and thermal conductive components in high-temperature heat treatment processes. In addition, graphite blocks can also be used as electrodes to carry out current transfer in electrolysis processes. Therefore, they are widely used as mechanical seals, thermal conductive materials and electrode materials in extreme environments such as high temperature, high pressure, and high speed.
Molding Technology
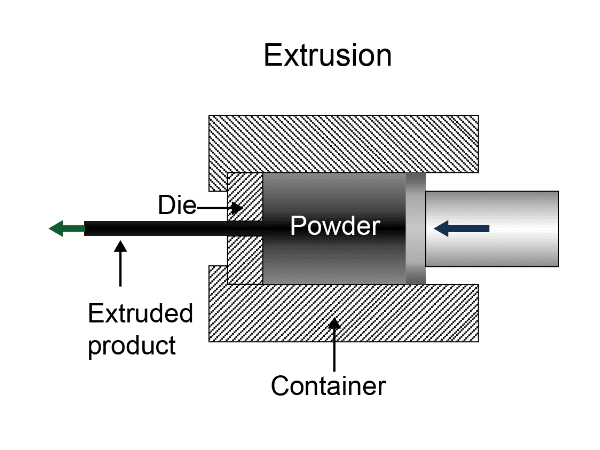
The extrusion method is to load the paste into the paste cylinder of the press and extrude it. The press is equipped with a replaceable extrusion ring (can be replaced to change the cross-sectional shape and size of the product) in front of it, and a movable baffle is provided in front of the extrusion ring. The main plunger of the press is located behind the paste cylinder.
Before applying pressure, place a baffle before the extrusion ring, and apply pressure from the opposite direction to compress the paste. When the baffle is removed and pressure is continued to be applied, the paste is extruded from the extrusion ring. Cut the extruded strip into the desired length, cool and inspect it before stacking. The extrusion method is a semi-continuous production process, which means that after a certain amount of paste is added, several (graphite blocks, graphite materials) products can be continuously extruded.
Currently, most carbon and graphite products are produced by extrusion method.
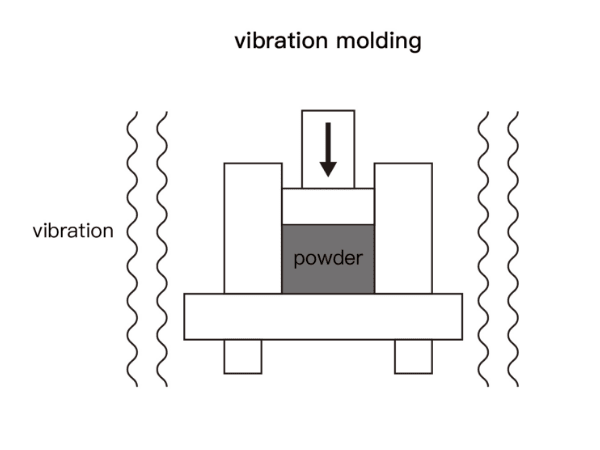
Vibrated graphite has a uniform structure with medium grain size. Besides, it becomes very popular because of its low ash content, enhanced mechanical strength, and good electrical and thermal stability, and is widely used for processing large-scale workpieces. It can also be further strengthened after resin impregnation or anti-oxidation treatment.
It is widely used as a heating & insulation element in the production of polysilicon and monocrystalline silicon furnaces in the photovoltaic industry. It is also widely used in manufacturing heating hoods, heat exchanger components, melting and casting crucibles, construction of n nodes used in electrolytic processes, and manufacturing of crucibles for melting and alloying.
Molding Technology
The principle of making vibrated graphite is to fill the mold with a paste-like mixture, and then place a heavy metal plate on top of it. In the next step, the material is compacted by vibrating the mold. Compared with extruded graphite, the graphite formed by vibration has higher isotropy. graphite products are produced by extrusion method.
Post time: Jun-17-2024