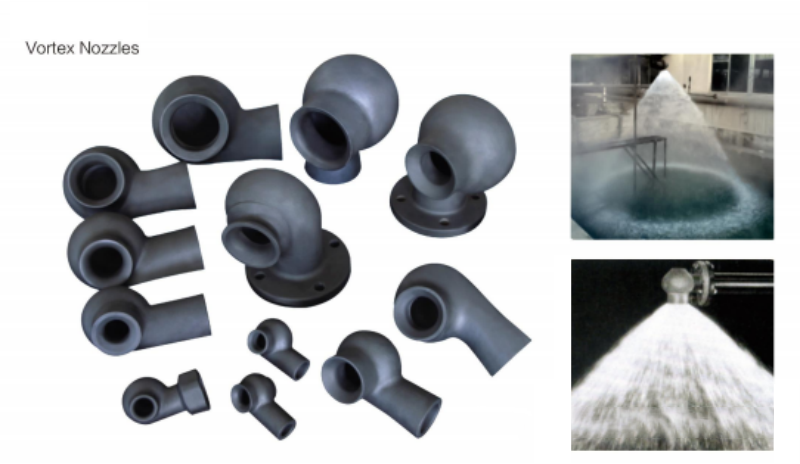
Reaction sintering
The reaction sintering silicon carbide ceramic production process includes ceramic compacting, sintering flux infiltration agent compacting, reaction sintering ceramic product preparation, silicon carbide wood ceramic preparation and other steps.
Reaction sintering silicon carbide nozzle
First, 80-90% of ceramic powder (composed of one or two powders of silicon carbide powder and boron carbide powder), 3-15% of carbon source powder (composed of one or two of carbon black and phenolic resin) and 5-15% of molding agent (phenolic resin, polyethylene glycol, hydroxymethyl cellulose or paraffin) are mixed evenly using a ball mill to obtain a mixed powder, which is spray dried and granulated, and then pressed in a mold to obtain a ceramic compact with various specific shapes.
Secondly, 60-80% silicon powder, 3-10% silicon carbide powder and 37-10% boron nitride powder are mixed evenly, and pressed in a mold to obtain a sintering flux infiltration agent compact.
The ceramic compact and the sintered infiltrant compact are then stacked together, and the temperature is raised to 1450-1750℃ in a vacuum furnace with a vacuum degree of not less than 5×10-1 Pa for sintering and heat preservation for 1-3 hours to obtain a reaction sintered ceramic product. The infiltrant residue on the surface of the sintered ceramic is removed by tapping to obtain a dense ceramic sheet, and the original shape of the compact is maintained.
Finally, the reaction sintering process is adopted, that is, liquid silicon or silicon alloy with reaction activity at high temperature infiltrates into the porous ceramic blank containing carbon under the action of capillary force, and reacts with the carbon therein to form silicon carbide, which will expand in volume, and the remaining pores are filled with elemental silicon. The porous ceramic blank can be pure carbon or silicon carbide/carbon-based composite material. The former is obtained by catalytically curing and pyrolyzing an organic resin, a pore former and a solvent. The latter is obtained by pyrolyzing silicon carbide particles/resin-based composite materials to obtain silicon carbide/carbon-based composite materials, or by using α-SiC and carbon powder as starting materials and using a pressing or injection molding process to obtain the composite material.
Pressureless sintering
The pressureless sintering process of silicon carbide can be divided into solid-phase sintering and liquid-phase sintering. In recent years, the research on silicon carbide ceramics at home and abroad has mainly focused on liquid-phase sintering. The ceramic preparation process is: mixed material ball milling–>spray granulation–>dry pressing–>green body solidification–>vacuum sintering.
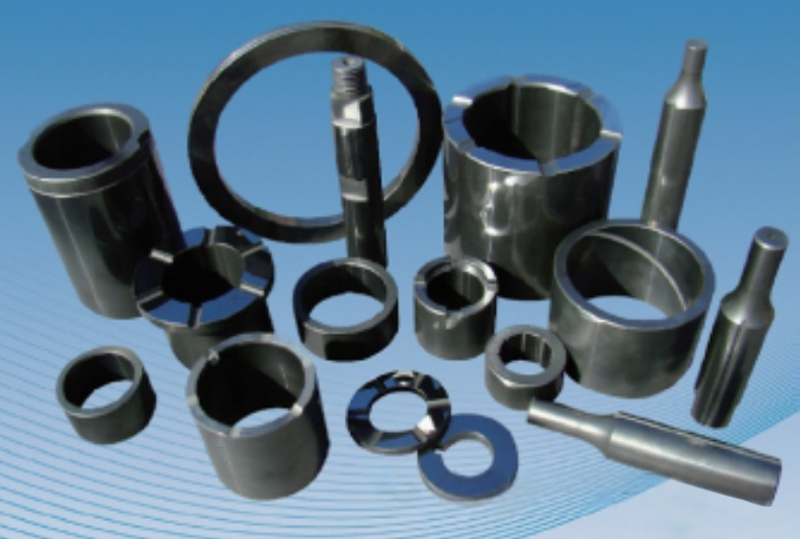

Pressureless sintered silicon carbide products
Add 96-99 parts of silicon carbide ultrafine powder (50-500nm), 1-2 parts of boron carbide ultrafine powder (50-500nm), 0.2-1 parts of nano-titanium boride (30-80nm), 10-20 parts of water-soluble phenolic resin, and 0.1-0.5 parts of high-efficiency dispersant to the ball mill for ball milling and mixing for 24 hours, and put the mixed slurry into a mixing barrel for stirring for 2 hours to remove bubbles in the slurry.
The above mixture is sprayed into the granulation tower, and the granulation powder with good particle morphology, good fluidity, narrow particle distribution range and moderate moisture is obtained by controlling the spray pressure, air inlet temperature, air outlet temperature and spray sheet particle size. The centrifugal frequency conversion is 26-32, the air inlet temperature is 250-280℃, the air outlet temperature is 100-120℃, and the slurry inlet pressure is 40-60.
The above granulation powder is placed in a cemented carbide mold for pressing to obtain a green body. The pressing method is bidirectional pressure, and the machine tool pressure tonnage is 150-200 tons.
The pressed green body is placed in a drying oven for drying and curing to obtain a green body with good green body strength.
The above cured green body is placed in a graphite crucible and arranged closely and neatly, and then the graphite crucible with the green body is placed in a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace for firing. The firing temperature is 2200-2250℃, and the insulation time is 1-2 hours. Finally, high-performance pressureless sintered silicon carbide ceramics are obtained.
Solid-phase sintering
The pressureless sintering process of silicon carbide can be divided into solid-phase sintering and liquid-phase sintering. Liquid-phase sintering requires the addition of sintering additives, such as Y2O3 binary and ternary additives, to make SiC and its composite materials present liquid-phase sintering and achieve densification at a lower temperature. The preparation method of solid-phase sintered silicon carbide ceramics includes mixing of raw materials, spray granulation, molding, and vacuum sintering. The specific production process is as follows:
70-90% of submicron α silicon carbide (200-500nm), 0.1-5% of boron carbide, 4-20% of resin, and 5-20% of organic binder are placed in a mixer and added with pure water for wet mixing. After 6-48 hours, the mixed slurry is passed through a 60-120 mesh sieve;
The sieved slurry is spray granulated through a spray granulation tower. The inlet temperature of the spray granulation tower is 180-260℃, and the outlet temperature is 60-120℃; the bulk density of the granulated material is 0.85-0.92g/cm3 , fluidity is 8-11s/30g; the granulated material is sieved through a 60-120 mesh sieve for later use;
Select a mold according to the desired product shape, load the granulated material into the mold cavity, and perform room temperature compression molding at a pressure of 50-200MPa to obtain a green body; or place the green body after compression molding into an isostatic pressing device, perform isostatic pressing at a pressure of 200-300MPa, and obtain a green body after secondary pressing;
Put the green body prepared in the above steps into a vacuum sintering furnace for sintering, and the qualified one is the finished silicon carbide bulletproof ceramic; in the above sintering process, first evacuate the sintering furnace, and when the vacuum degree reaches 3-5×10-2 After Pa, the inert gas is passed into the sintering furnace to normal pressure and then heated. The relationship between heating temperature and time is: room temperature to 800℃, 5-8 hours, heat preservation for 0.5-1 hour, from 800℃ to 2000-2300℃, 6-9 hours, heat preservation for 1 to 2 hours, and then cooled with the furnace and dropped to room temperature.
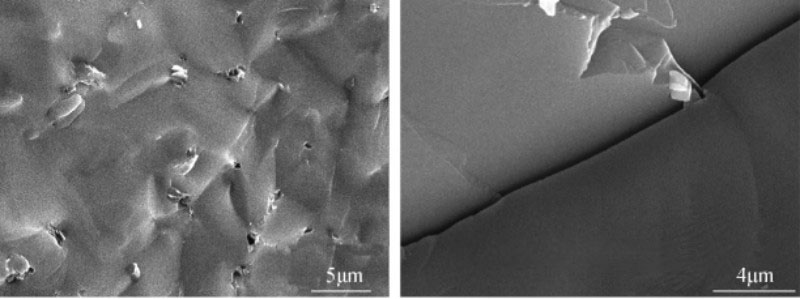
Microstructure and grain boundary of silicon carbide sintered at normal pressure
In short, ceramics manufactured by hot pressing sintering process have better performance, but the production cost is also greatly increased; ceramics prepared by pressureless sintering have higher raw material requirements, high sintering temperature, large product size changes, complex process and low performance; ceramic products produced by reaction sintering process have high density, good anti-ballistic performance, and relatively low preparation cost. Various sintering preparation processes of silicon carbide ceramics have their own advantages and disadvantages, and the application scenarios will also be different. It is the best policy to choose the right preparation method according to the product and find a balance between low cost and high performance.
Post time: Oct-29-2024

