Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is the most widely used technology in the semiconductor industry for depositing a variety of materials, including a wide range of insulating materials, most metal materials and metal alloy materials.
CVD is a traditional thin film preparation technology. Its principle is to use gaseous precursors to decompose certain components in the precursor through chemical reactions between atoms and molecules, and then form a thin film on the substrate. The basic characteristics of CVD are: chemical changes (chemical reactions or thermal decomposition); all materials in the film come from external sources; reactants must participate in the reaction in the form of gas phase.
Low pressure chemical vapor deposition (LPCVD), plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) and high density plasma chemical vapor deposition (HDP-CVD) are three common CVD technologies, which have significant differences in material deposition, equipment requirements, process conditions, etc. The following is a simple explanation and comparison of these three technologies.
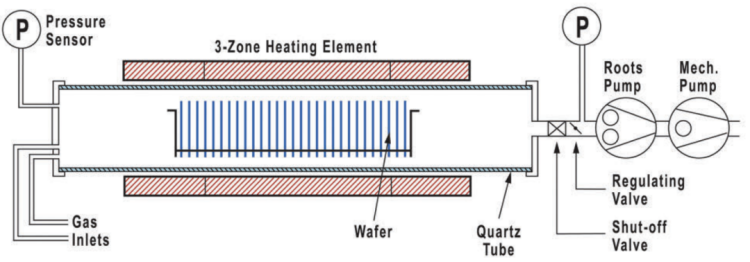
1. LPCVD (Low Pressure CVD)
Principle: A CVD process under low pressure conditions. Its principle is to inject the reaction gas into the reaction chamber under vacuum or low pressure environment, decompose or react the gas by high temperature, and form a solid film deposited on the substrate surface. Since the low pressure reduces gas collision and turbulence, the uniformity and quality of the film are improved. LPCVD is widely used in silicon dioxide (LTO TEOS), silicon nitride (Si3N4), polysilicon (POLY), phosphosilicate glass (BSG), borophosphosilicate glass (BPSG), doped polysilicon, graphene, carbon nanotubes and other films.
Features:
▪ Process temperature: usually between 500~900°C, the process temperature is relatively high;
▪ Gas pressure range: low pressure environment of 0.1~10 Torr;
▪ Film quality: high quality, good uniformity, good density, and few defects;
▪ Deposition rate: slow deposition rate;
▪ Uniformity: suitable for large-size substrates, uniform deposition;
Advantages and disadvantages:
▪ Can deposit very uniform and dense films;
▪ Performs well on large-size substrates, suitable for mass production;
▪ Low cost;
▪ High temperature, not suitable for heat-sensitive materials;
▪ Deposition rate is slow and the output is relatively low.
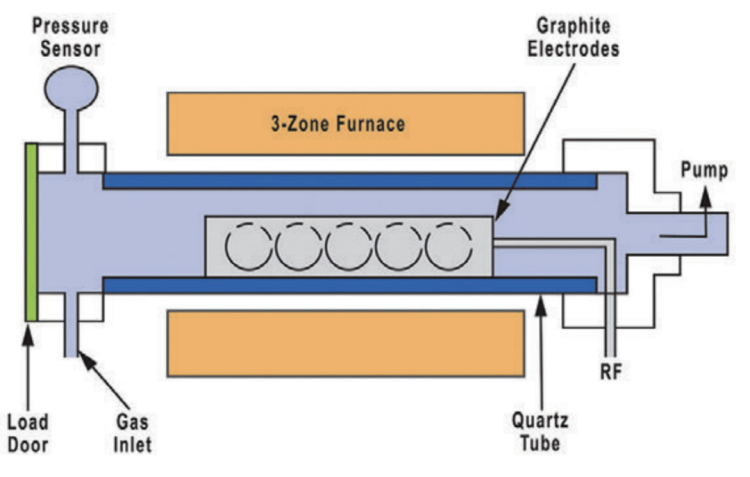
2. PECVD (Plasma Enhanced CVD)
Principle: Use plasma to activate gas phase reactions at lower temperatures, ionize and decompose the molecules in the reaction gas, and then deposit thin films on the substrate surface. The energy of plasma can greatly reduce the temperature required for the reaction, and has a wide range of applications. Various metal films, inorganic films and organic films can be prepared.
Features:
▪ Process temperature: usually between 200~400°C, the temperature is relatively low;
▪ Gas pressure range: usually hundreds of mTorr to several Torr;
▪ Film quality: although the film uniformity is good, the density and quality of the film are not as good as LPCVD due to defects that may be introduced by plasma;
▪ Deposition rate: high rate, high production efficiency;
▪ Uniformity: slightly inferior to LPCVD on large-size substrates;
Advantages and disadvantages:
▪ Thin films can be deposited at lower temperatures, suitable for heat-sensitive materials;
▪ Fast deposition speed, suitable for efficient production;
▪ Flexible process, film properties can be controlled by adjusting plasma parameters;
▪ Plasma may introduce film defects such as pinholes or non-uniformity;
▪ Compared with LPCVD, the film density and quality are slightly worse.
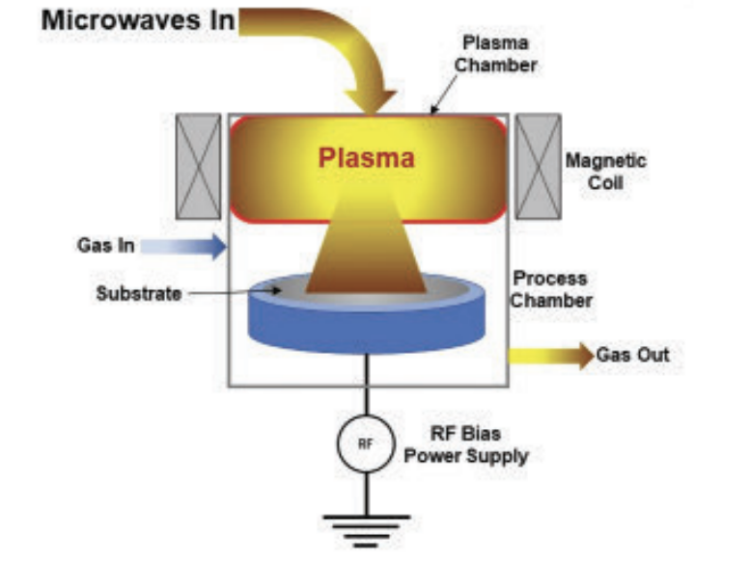
3. HDP-CVD (High Density Plasma CVD)
Principle: A special PECVD technology. HDP-CVD (also known as ICP-CVD) can produce higher plasma density and quality than traditional PECVD equipment at lower deposition temperatures. In addition, HDP-CVD provides almost independent ion flux and energy control, improving trench or hole filling capabilities for demanding film deposition, such as anti-reflective coatings, low dielectric constant material deposition, etc.
Features:
▪ Process temperature: room temperature to 300℃, the process temperature is very low;
▪ Gas pressure range: between 1 and 100 mTorr, lower than PECVD;
▪ Film quality: high plasma density, high film quality, good uniformity;
▪ Deposition rate: deposition rate is between LPCVD and PECVD, slightly higher than LPCVD;
▪ Uniformity: due to high-density plasma, film uniformity is excellent, suitable for complex-shaped substrate surfaces;
Advantages and disadvantages:
▪ Capable of depositing high-quality films at lower temperatures, very suitable for heat-sensitive materials;
▪ Excellent film uniformity, density and surface smoothness;
▪ Higher plasma density improves deposition uniformity and film properties;
▪ Complicated equipment and higher cost;
▪ Deposition speed is slow, and higher plasma energy may introduce a small amount of damage.
Welcome any customers from all over the world to visit us for a further discussion!
https://www.vet-china.com/
https://www.facebook.com/people/Ningbo-Miami-Advanced-Material-Technology-Co-Ltd/100085673110923/
https://www.linkedin.com/company/100890232/admin/page-posts/published/
https://www.youtube.com/@user-oo9nl2qp6j
Post time: Dec-03-2024